Connect external models
Snorkel supports connecting third-party foundation models, like OpenAI and Claude, to run inference-related workflows like evaluation, on the Snorkel AI Data Development Platform.
To connect to external models, follow these steps:
- Create an account with the third-party service provider.
- Configure a connection to that service within your Snorkel instance.
This connection setup allows all workflows in your instance to access the third-party models for inference operations.
Prerequisites
- An account and credentials with the providers you want to connect
How to connect external services
You can connect external integrations to your Snorkel instance. The Snorkel secrets service securely manages stored API keys and secrets.
Connect to model providers using the Snorkel GUI
Prerequisites:
- Log in to Snorkel with superadmin permissions
-
In the Snorkel GUI, select your profile.
-
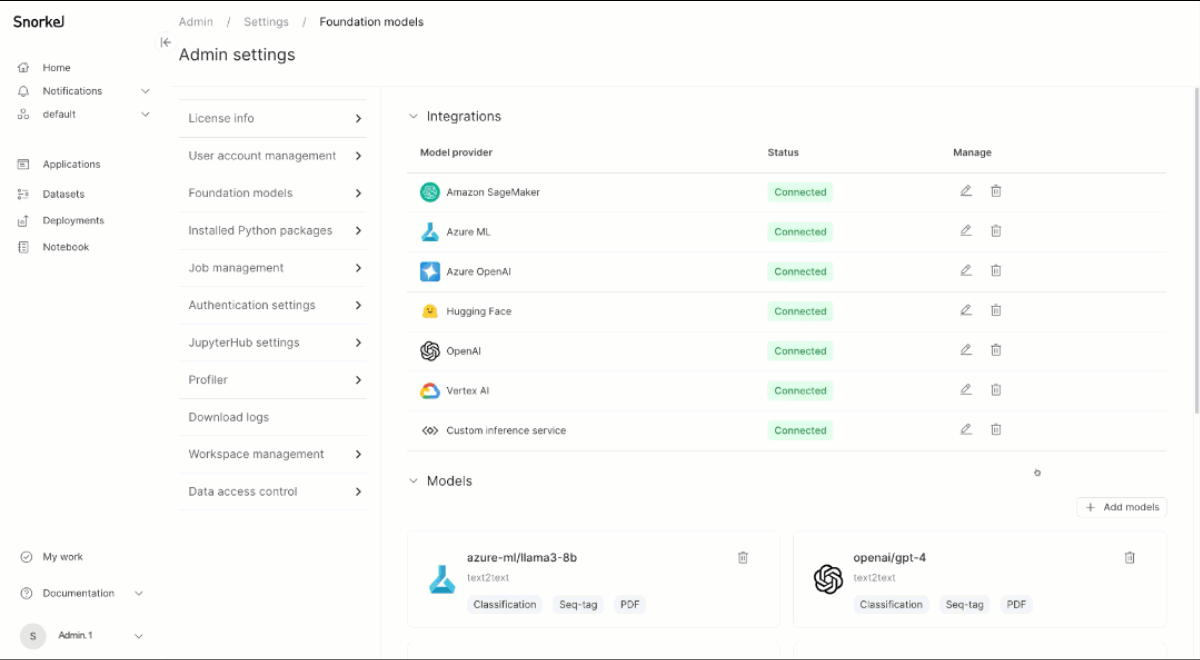
Select Admin Settings > Foundation Models.
-
Select Connect for the integration you want to add.
-
Enter the required details from your external integration provider and select Save.
-
Configure available models for the provider you added.
-
(Optional) To make changes, select the Edit or Delete button for your integration.
warningDeleting an integration also deletes all models associated with that integration.
Connect to model providers using the SDK
-
To list the integrations that are currently connected, use this SDK command:
sai.list_integrations() -
To check the operational status of an integration, use the
get_model_provider_statuscommand for your associated provider:sai.get_model_provider_status(ExternalLLMProvider.OPENAI) -
To add a connection to a new integration, use the
set_secretcommand for your supported services:-
Hugging Face
sai.set_secret("huggingface::inference::api_token", "**YOUR API KEY**")For more, see Hugging Face token settings.
-
OpenAI
sai.set_secret("openai_api_key", "**YOUR API KEY**")For more, see OpenAI API keys.
-
Azure OpenAI
sai.set_secret("azure_openai_api_key", "**YOUR API KEY**") -
Azure Machine Learning
sai.set_secret("azure::ml::api_key", "**YOUR API KEY**") -
Vertex AI
sai.set_secret("vertexai_lm_location", "**YOUR PROJECT LOCATION**")
sai.set_secret("vertexai_lm_project_id", "**YOUR PROJECT ID**")
sai.set_secret("vertexai_lm_credentials_json", "**YOUR CREDENTIALS JSON**") -
Amazon SageMaker
sai.set_secret("aws::finetuning::region", "**YOUR REGION**")
sai.set_secret("aws::finetuning::access_key_id", "**YOUR ACCESS KEY ID**")
sai.set_secret("aws::finetuning::secret_access_key", "**YOUR SECRET ACCESS KEY**")
sai.set_secret("aws::finetuning::sagemaker_execution_role", "**YOUR EXECUTION ROLE**") -
Amazon Bedrock
sai.set_secret("aws::bedrock::region", "**YOUR REGION**")
sai.set_secret("aws::bedrock::access_key_id", "**YOUR ACCESS KEY ID**")
sai.set_secret("aws::bedrock::secret_access_key", "**YOUR SECRET ACCESS KEY**")
sai.set_secret("aws::bedrock::bedrock_execution_role", "**YOUR EXECUTION ROLE**") -
Custom inference service: see Custom Inference Service API
-
How to add models in Snorkel
After you connect an external service to Snorkel, you can add the models from that service to Snorkel.
Add models using the Snorkel GUI
- In the Snorkel GUI, select your profile.
- Select Admin Settings > Foundation Models.
- Select the Add models button.
- From the dropdown, choose the model provider you set up in the previous step. Enter the details for Model type, Model name, and Endpoint URL.
The model you added is now visible in the Models section and is available for use in Snorkel.
Add models using the SDK
To view the models that are currently connected, use this SDK command:
sai.get_external_model_endpoints()
You can view detailed information about configured models using the detail parameter:
sai.get_external_model_endpoints(detail=True)
You can inspect configuration information for a particular model using the model_name parameter:
sai.get_external_model_endpoints(model_name="openai/gpt-4o", detail=True)
To add models to Snorkel, include the following information for each model:
-
model_name: The name of the provider followed by the name of the model. For example,openai/gpt-4. -
endpoint: The endpoint to perform inference requests. -
model_provider: The provider serving the model. For example, Hugging Face, OpenAI, Vertex AI, or a custom inference service. -
fm_type: The associated task type for the model.This example shows how to add the
openai/gpt-4omodel to Snorkel:from snorkelai.client.tdm.models import ExternalLLMProvider, FMType
sai.set_external_model_endpoint(
model_name="openai/gpt-4o", # Compatible chat completions model
endpoint="https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions", # Chat completions endpoint
model_provider=ExternalLLMProvider.OPENAI, # Model provider
fm_type=FMType.TEXT2TEXT, # The task type of the model
)
To delete a configured model, use this SDK command:
sai.delete_external_model_endpoint("openai/gpt-4o")
Hugging Face 🤗 inference endpoints
To add a Hugging Face model, launch your chosen Hugging Face model on their servers using Hugging Face endpoints. You will be given an endpoint URL for that model.
This example shows how to set up a Hugging Face Text2Text model for Prompt Dev applications:
sai.set_external_model_endpoint(
model_name="**MODEL NAME**", # Set this to the model you have created the endpoint for
endpoint="**ENDPOINT URL**", # Set this to the URL for the model found in the Inference Endpoints Dashboard
model_provider=ExternalLLMProvider.HUGGINGFACE, # Model provider
fm_type=FMType.TEXT2TEXT, # The task type of the model; in this case, text2text
)
OpenAI API
To add an Open AI model, set up your API token and ensure that you are using the appropriate API endpoint. Specify a chat completions endpoint for chat models or a completions endpoint for language models. For more information about what API endpoint a model belongs, see OpenAI's Text generation models documentation.
This example shows how to configure an OpenAI model with the chat completions API endpoint:
sai.set_external_model_endpoint(
model_name="openai/o1-mini", # Compatible chat completions model
endpoint="https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions", # Chat completions endpoint
model_provider=ExternalLLMProvider.OPENAI, # Model provider
fm_type=FMType.TEXT2TEXT, # The task type of the model
)
This example shows how to configure an OpenAI model with the legacy completions API endpoint:
sai.set_external_model_endpoint(
model_name="openai/gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct", # Compatible completions model
endpoint="https://api.openai.com/v1/completions", # Completions endpoint
model_provider=ExternalLLMProvider.OPENAI, # Model provider
fm_type=FMType.TEXT2TEXT, # The task type of the model
)
Azure OpenAI API
To add an Azure OpenAI model, set up your API token and ensure that you are using the appropriate API endpoint.
This example shows how to configure a supported Azure OpenAI chat model.
sai.set_external_model_endpoint(
model_name="azure_openai/your-deployment-name", # Compatible chat completions model
endpoint="https://your-instance-name.openai.azure.com/chat/completions", # Chat completions endpoint
model_provider=ExternalLLMProvider.AZURE_OPENAI, # Model provider
fm_type=FMType.TEXT2TEXT, # The task type of the model
)
Azure Machine Learning API
To add an Azure Machine Learning AI model, set up your API token and ensure that you are using the appropriate API endpoint.
This example shows how to configure a supported Azure Machine Learning model.
from snorkelai.models.prompts.prompts_services.azure import AzureDataInferenceInterfaceTypes
sai.set_external_model_endpoint(
model_name="your-model-name", # Name of your deployed Azure ML model
endpoint="https://<deployment-name>.westus2.inference.ml.azure.com/score", # Chat completions endpoint
model_provider=ExternalLLMProvider.AZURE_ML, # Model provider
fm_type=FMType.TEXT2TEXT, # The task type of the model
azure_task_type=AzureDataInferenceInterfaceTypes.Llama.value,
)
Bedrock Claude API
To add a Bedrock Claude model endpoint:
sai.set_external_model_endpoint(
model_name="bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022-v2:0", # Model name
endpoint="bedrock-runtime.us-west-2.amazonaws.com", # Endpoint
model_provider=ExternalLLMProvider.Bedrock, # Model provider
fm_type=FMType.TEXT2TEXT, # The task type of the model
)
Supported Claude models
The following models are currently supported via AWS Bedrock:
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet v2
- Claude 3.7
View the Model IDs here.
Vertex AI language models API
To add a Vertex AI model, set up your Vertex AI location, project ID, and credentials JSON.
This example shows how to configure a Vertex AI model:
sai.set_external_model_endpoint(
model_name="vertexai_lm/gemini-1.5-pro-002", # Model name
endpoint="https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai", # Endpoint
model_provider=ExternalLLMProvider.VERTEXAI_LM, # Model provider
fm_type=FMType.TEXT2TEXT, # The task type of the model
)
Amazon SageMaker API
To add an Amazon Sagemaker model endpoint for predictive use cases:
sai.set_external_model_endpoint(
model_name="sagemaker/jumpstart-dft-meta-textgeneration-llama-3-8b-instruct", # Model name
endpoint="https://runtime.sagemaker.<region-name>.amazonaws.com/endpoints/jumpstart-dft-meta-textgeneration-llama-3-8b-instruct/invocations", # Endpoint
model_provider=ExternalLLMProvider.SAGEMAKER, # Model provider
fm_type=FMType.TEXT2TEXT, # The task type of the model
)
Custom inference service API
The custom inference service enables users to configure custom endpoints and additional foundation model providers.
OpenAI-compatible services
The custom inference service supports endpoints from foundation model providers that follow the OpenAI API schema, such as Together AI, Groq, and others. To integrate a supported model: OpenAI API specification.
1. Set API secrets
sai.set_secret("custom_inference_api_key", "**YOUR API KEY**")
# Optional: Set default HTTP headers. Note: if authentication is is not via
sai.set_secret("custom_inference_optional_headers", {
"**HEADER_NAME**": "**HEADER_VALUE**"
})
NOTE: By default, custom_inference_api_key is used as a Bearer token in the Authorization header for requests (i.e.Authorization: Bearer <custom_inference_api_key>).
If your service uses a different or additional authentication method, set the correct headers using custom_inference_optional_headers.
However, you still need to provide an arbitrary value for custom_inference_api_key.
2. Register model endpoints
After setting up your custom inference API key, add a model with custom inference service that conforms to the OpenAI API specification. Like the OpenAI setup, specify a chat completions endpoint for chat models or a completions endpoint for language models. This inference service is also extensible to other foundation model providers that conform to OpenAI's API specification, such as Together AI.
This example shows how to set up a supported model with the chat completions API endpoint:
sai.set_external_model_endpoint(
model_name="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-Turbo", # Chat model
endpoint="https://api.together.xyz/v1/chat/completions", # Inference service chat endpoint
model_provider=ExternalLLMProvider.CUSTOM_INFERENCE_SERVICE, # Model provider
fm_type=FMType.TEXT2TEXT, # The task type of the model
)
This example shows how to set up a supported model with the completions API endpoint:
sai.set_external_model_endpoint(
model_name="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B", # Language model
endpoint="https://api.together.xyz/v1/completions", # Inference service completions endpoint
model_provider=ExternalLLMProvider.CUSTOM_INFERENCE_SERVICE, # Model provider
fm_type=FMType.TEXT2TEXT, # The task type of the model
)
Non-OpenAI-compatible services
If your external inference service does not conform to the OpenAI API spec, you can still integrate it using a transform configuration. This allows Snorkel to map requests and responses between OpenAI-compatible schemas and your custom API.
Steps:
- Set the
custom_inference_api_keyandcustom_inference_optional_headerssecrets as above. - Create a transform configuration: The transform configuration is a JSON object with the following required fields:
-
/chat/completions:
The root key representing the OpenAI endpoint you wish to transform. This key defines which OpenAI endpoint's requests/responses will be mapped. -
custom_path:
The path on your custom LLM API that corresponds to the OpenAI/chat/completionsendpoint. Snorkel routes requests to this path instead of the default OpenAI endpoint. -
openai_to_custom_request:
An object that defines how to transform the OpenAI request JSON into the format expected by your custom LLM API.- Keys: Field names as expected by your custom API. - Values: JMESPath expressions describing how to extract or map values from the OpenAI request schema.
-
custom_to_openai_response:
An object that defines how to transform your custom LLM API's response into the OpenAI response schema.- Keys: Field names as expected by the OpenAI API/SDK.
- Values: JMESPath expressions describing how to extract or map values from your custom API's response.
When configuring a Custom Inference Services with a transform spec and associated models, set the base URL for the custom inference service
endpoint(do not include the chat completions path). Instead add the chat completion path to thecustom_pathfield in the transform configuration.Example transform configuration:
import json
transform_config = {
"/chat/completions": {
"custom_path": "/v1/generate",
"openai_to_custom_request": {
"useCase": "'text-generation'",
"contextId": "model",
"preSeed_injection_map": {
"system": "messages[?role=='system'].content | join(' ', @)",
"user": "messages[?role=='user'].content | join(' ', @)"
},
"parameters": {
"temperature": "temperature",
"maxOutputTokens": "max_tokens",
"topP": "top_p",
"responseMimeType": "'application/json'"
}
},
"custom_to_openai_response": {
"id": "responseMetadata.vegasTransactionId",
"model": "responseMetadata.llmResponsePayload[0].modelVersion",
"choices": "[{index: to_number('0'), message: {role: 'assistant', content: responseMetadata.llmResponsePayload[0].candidates[0].content.parts[0].text}, finish_reason: responseMetadata.llmResponsePayload[0].finishReason == 'STOP' && 'stop' || 'length'}]",
"usage": {
"prompt_tokens": "responseMetadata.llmResponsePayload[0].usageMetadata.promptTokenCount || to_number('0')",
"completion_tokens": "responseMetadata.llmResponsePayload[0].usageMetadata.candidatesTokenCount || to_number('0')",
"total_tokens": "responseMetadata.llmResponsePayload[0].usageMetadata.totalTokenCount || to_number('0')"
}
}
}
}
sai.set_secret("custom_inference_transform_spec", json.dumps(transform_config))
How to specify model hyper-parameters
Snorkel supports the setting of arbitrary model hyper-parameters when you configure a model in Snorkel. Some example parameters that this include are:
temperaturetop_pmax_input_lengthmax_output_length
When setting a model hyper-parameter, please ensure it appears exactly as documented by the model's provider. For example, when configuring the temperature hyper-parameter, some models leverage the keyword temp, others use t, and some require the full word temperature.
Once you have confirmed the hyper-parameter names and values you'd like to set,
provide them as keyword arguments to sai.set_external_model_endpoint. For
example, to set temperature and max_tokens on openai/gpt-4o, run:
sai.set_external_model_endpoint(
model_name="openai/gpt-4o", # Compatible chat completions model
endpoint="https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions", # Chat completions endpoint
model_provider=ExternalLLMProvider.OPENAI, # Model provider
fm_type=FMType.TEXT2TEXT, # The task type of the model
temperature=0.5,
max_tokens=500,
)
How to set rate limits
Snorkel supports custom rate limits for the OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Bedrock, and custom inference service integrations.
To enable this feature, use the SDK function sai.set_external_model_endpoint()
to configure the requests_per_sec and tokens_per_sec parameters. Snorkel
consumes as much as the provided quota when computing previews of prompt LFs
for the whole Snorkel instance.
When setting these values, get the correct values from your organization’s usage tier and provide the values in per-second level. If you provide incorrect values, Snorkel might hit rate limits for OpenAI or underutilize the provided quota.
To determine OpenAI usage limits, visit the OpenAI organization limits
page. Find the
token limits and request limits per minute for your desired model and
divide it by 60 to compute the per-second value. For example, when the model
gpt-4o-mini shows 10,000 RPM for request and other limits and 30,000,000 TPM
for token limits, provide requests_per_sec=166 and tokens_per_sec=500000 as
extra keyword arguments in the set_external_model_endpoint() function.
Here is an example for configuring gpt-4o-mini with rate limits:
# delete an existing model endpoint, only if already registered
sai.delete_external_model_endpoint("openai/gpt-4o-mini")
sai.set_external_model_endpoint(
model_name="openai/gpt-4o-mini", # Compatible chat completions model
endpoint="https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions", # Chat completions endpoint
model_provider=ExternalLLMProvider.OPENAI, # Model provider
fm_type=FMType.TEXT2TEXT, # The task type of the model
requests_per_sec=166, # request limit per second
tokens_per_sec=500000, # token limit per second
)