Walkthrough for reviewers
This guide walks you through the reviewer workflow within annotation tasks. As a reviewer, you can evaluate annotations from multiple annotators and commit final decisions to ground truth.
As a reviewer, you may also need to annotate documents yourself. See the Annotator workflow for step-by-step annotation instructions.
Getting started with reviewer mode
Accessing reviewer mode
Reviewer mode is available in the annotation data viewer. There are two ways to navigate to the annotation data viewer:
- From the Annotate tab: Click Annotate in the left-side menu, then select your task from the list
- From the Datasets page: Click Datasets in the left-side menu, select your dataset, go to the Annotation Tasks tab, then click the annotate icon in the table for your task
Once you're in the annotation data viewer for a task where you have reviewer permissions, toggle the Reviewer mode on and off to switch between:
- Annotation view: Your personal annotation interface
- Reviewer view: Interface showing all datapoints with annotator submissions for review
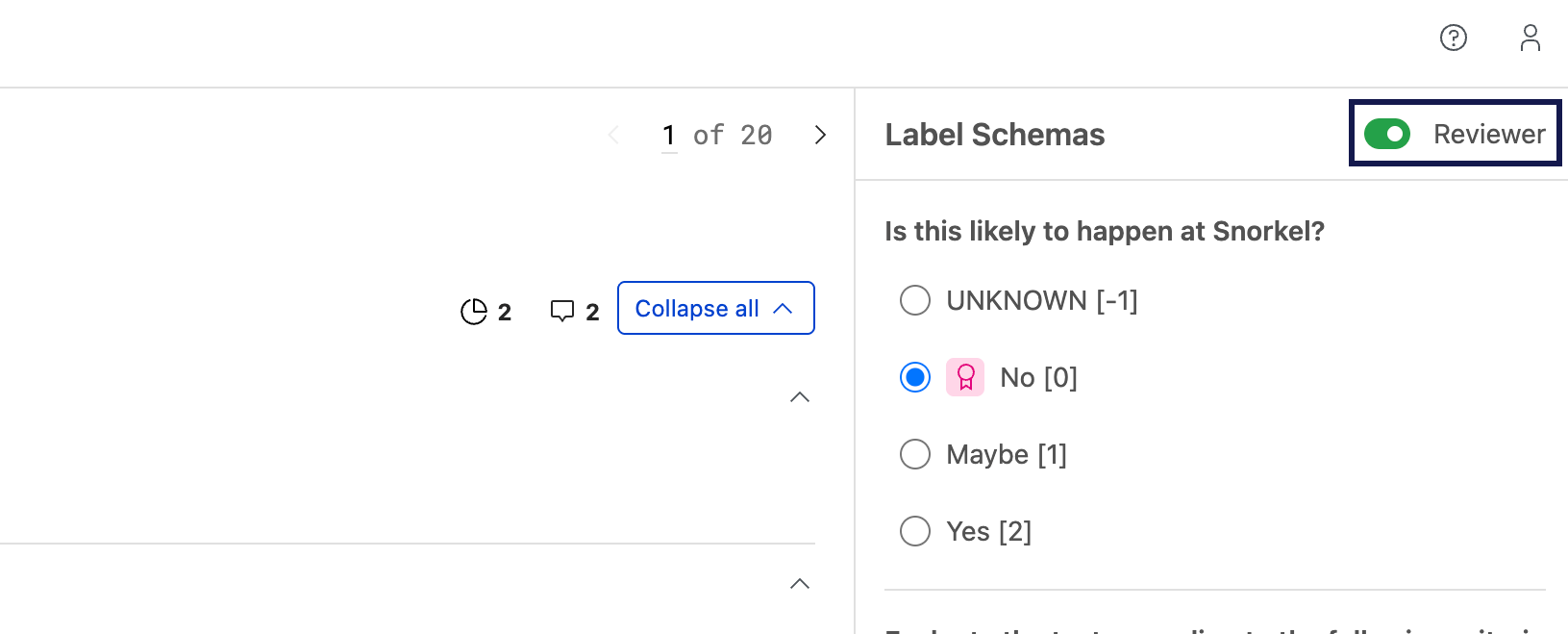
Understanding datapoint status
Each datapoint progresses through these status stages:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Needs assignees | Minimum number of required annotators annotators have not been assigned to this datapoint |
| In annotation | Annotators are currently working on this datapoint |
| Ready for review | Minimum number of required annotators have completed their work and the datapoint awaits your review |
| Completed | You have reviewed and committed the annotations to ground truth |
Filtering and finding datapoints
Use the filtering options to focus your review efforts on specific datapoints based on your workflow needs. Filter by Ready for review status to see only datapoints that have completed annotations and are waiting for your review. This helps you efficiently manage large annotation tasks by viewing targeted subsets of data.
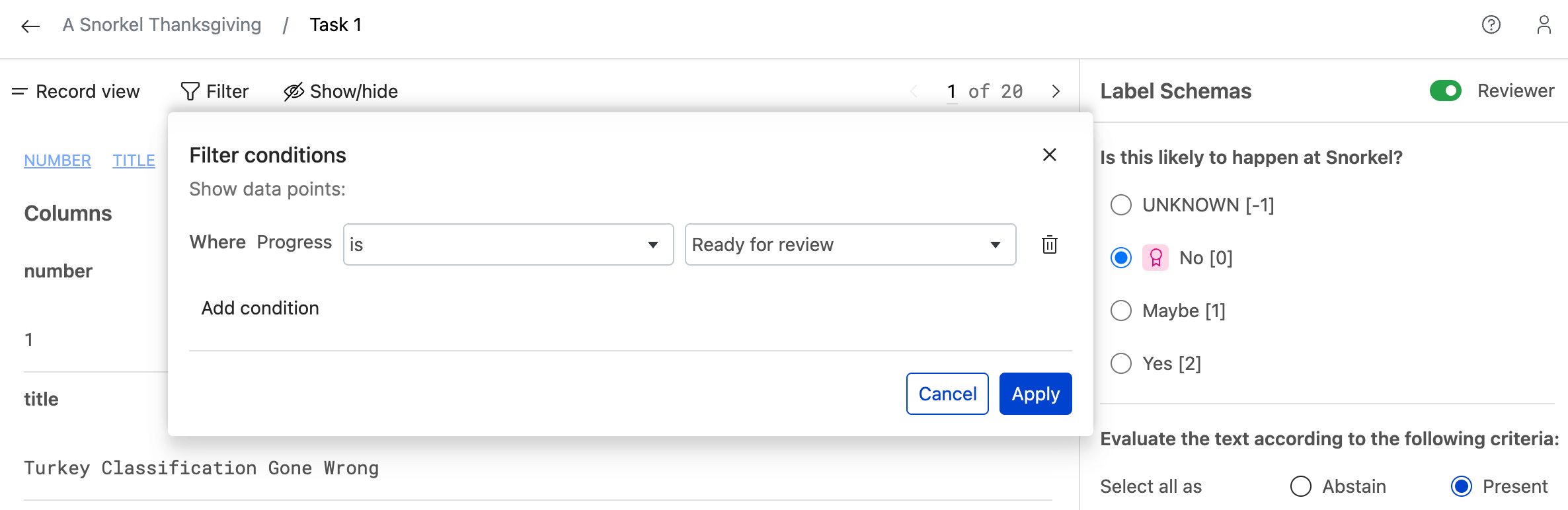
Reviewing annotations
Review tools and interactions
While reviewing annotations, you have access to several tools:
- Comments: Add explanations for why you agree or disagree with specific annotations. Access this tool via the comment
icon in the top right corner of the document.
- Slices: Create document slices (e.g., "contains-disagreements") to categorize datapoints. Add or manage slices by clicking the slice
icon in the top right corner of the document.
Reviewing different question types
The review interface adapts based on your task's label schema configuration. Learn how to review each question type:
- Reviewing single-label questions
- Reviewing multi-label questions
- Reviewing text label questions
- Reviewing sequence tagging questions
Finalizing ground truth
When you're ready to commit
After reviewing all annotator submissions and making your decisions, you'll finalize the ground truth for each datapoint.
Commit requirements:
- Complete all questions for the datapoint by making your selections
- The commit button will turn blue when the datapoint is ready to commit
Committing ground truth
When you press the Commit button:
-
Initial commit:
- Your selections are saved as ground truth with pink badges marking each committed label
- A timestamp appears showing exactly when you committed
- The datapoint status changes to Completed
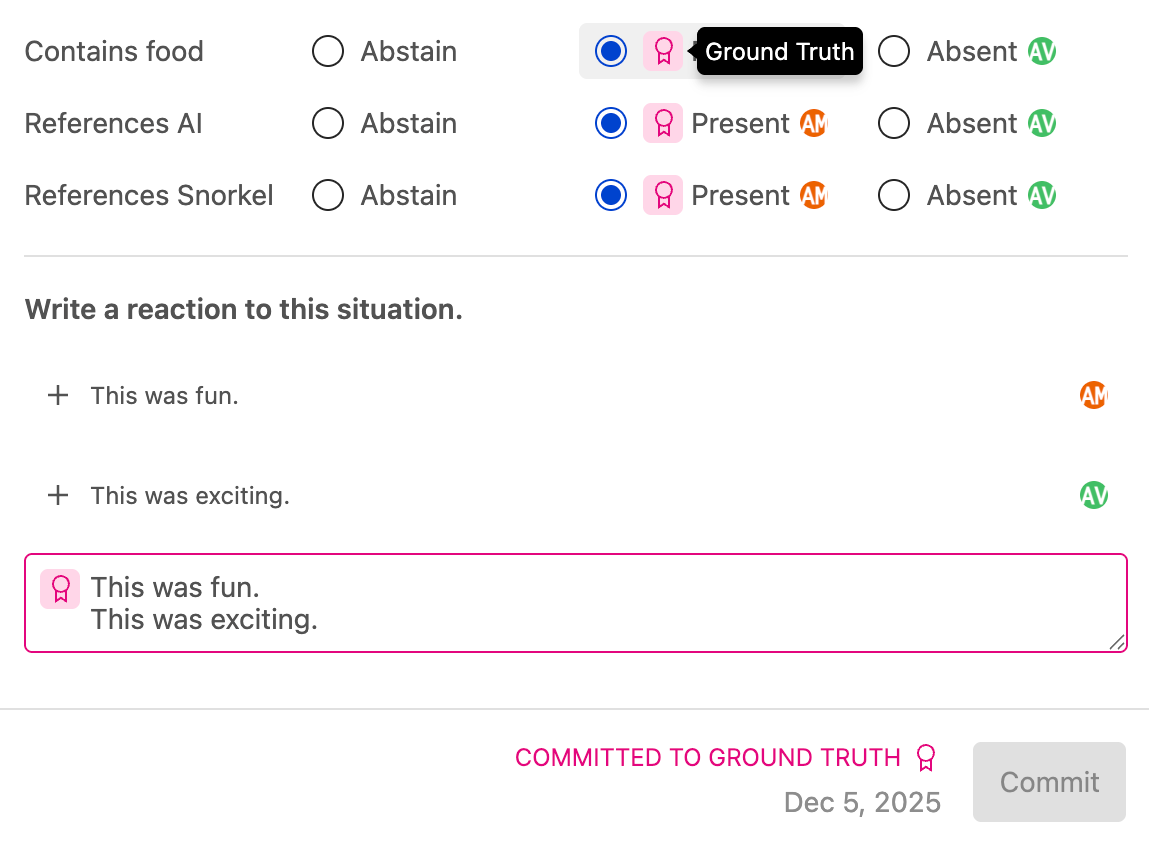
-
Making changes after commit:
- Modify your selections as needed
- Press Commit again to update
- Timestamp updates to show the latest commit
- Pink ground truth badges will update to reflect your new selections
- Status stays Completed
Working with existing ground truth
Some datapoints may already have ground truth from:
- Data imports
- Other tasks on same datapoints
What you'll see:
- Pink ground truth badge indicating existing ground truth
- Datapoint will not show as Completed for this specific task
What you need to do:
- Review the existing ground truth and correct any errors
- Press Commit to mark the datapoint as completed in this task context
- This confirms this datapoint is completed for your current task
- For tasks with many datapoints that have existing ground truth, you can use the SDK to complete multiple datapoints at once rather than completing each one individually